Rapid prototyping revolutionizes metal manufacturing by accelerating product development and reducing costs. We accomplish this by leveraging advanced technologies and continuous R&D, which offers benefits like design validation, time savings, and customized solutions across various industries.
As precision metal manufacturing continues to evolve, high-quality products are progressing through the manufacturing process faster than ever before.
What’s driving this progression? The rapid prototyping of metal parts.
Rapid prototyping is a pivotal technique within precision metal manufacturing, accelerating product development and allowing quality, precise components to progress from design to production to market at incredible speed. From aerospace to medical devices, the ability to swiftly produce and assess metal prototypes has changed the game, allowing manufacturers to stay ahead in highly competitive markets.
The secret to rapid prototyping lies in R&D. By continuously investing in R&D efforts, manufacturers can explore and implement cutting-edge technologies and innovative processes that accelerate the prototyping journey.
With a long history of working hand-in-hand with customers in highly innovative, technically demanding, and critical industries, E-Fab leads the way in rapid prototyping techniques and technologies. With specialist metal prototyping tools and equipment, including computer-aided design (CAD) software and other prototyping technologies, together with our specialist in-house engineering team, we’re continuing to drive innovation, efficiency, and quality in precision manufacturing for a variety of metal materials.
In this article, we delve into the development of high-quality metal components through metal prototyping and explore the crucial role R&D plays in driving this innovative new era of metal manufacturing.
What is Rapid Prototyping Metal Parts?
In the world of metal fabrication or additive manufacturing, rapid prototyping refers to the accelerated process of creating physical, functional metal prototypes of metal components or parts.
It involves using cutting-edge technology and techniques, such as photochemical etching, CNC machining, lost wax casting, investment casting, and laser cutting, to swiftly translate design concepts into a tangible metal prototype, allowing engineers and manufacturers to evaluate the feasibility, form, and functionality of their metal parts before committing to full-scale production.
Rapid prototyping has become critical in a wide range of industries — especially those with short product life cycles or intense competition- by reducing time-to-market, minimizing errors, and enabling precise iteration.
The Advantages of Rapid Prototyping
Manufacturing precision metal parts through rapid prototyping offers numerous benefits to engineers and manufacturers alike.
Metal prototyping enables engineers and manufacturers to swiftly assess the feasibility and design of intricate components, significantly reducing development lead times. It also allows for early detection and rectification of design flaws, ensuring the final metal prototypes are optimized for performance. The process also paves the way for precise metal casting, resulting in components with exceptional accuracy and integrity.
Key advantages of metal prototyping include:
Design Validation:
Rapid prototyping allows manufacturers to create physical product prototypes quickly, allowing them to validate and test the design before committing to large-scale production. By physically interacting with the prototype, engineers and designers can identify potential design flaws, functionality issues, or improvements that need to be made early in the development process.
Time and Cost Savings:
Rapid prototyping technologies significantly reduce lead times and costs for tooling and production setup by removing the constraints associated with traditional manufacturing processes. With rapid prototyping, manufacturers can quickly produce prototypes without expensive tooling or complex setup procedures, saving time and money in the development phase.

Iterative Design:
Boasting an iterative design process, rapid prototyping enables the creating and evaluating of multiple product iterations. Manufacturers can refine and improve their designs by quickly producing and testing numerous prototypes based on real-world feedback. This iterative approach helps identify and address design flaws, enhance functionality, and optimize performance, leading to a better final product.
Communication and Collaboration:
Prototypes provide tangible objects shared and communicated between designers, engineers, marketers, and clients. The prototypes facilitate effective communication and collaboration by providing an understanding of the product’s form, functionality, and aesthetics. Interacting with the prototype allows stakeholders to quickly provide feedback, make suggestions, and identify potential improvements.

Faster Time to Market:
Rapid prototyping accelerates the product development cycle, reducing the time it takes to bring a new product to market. Manufacturers can accelerate the overall development process by quickly validating and refining designs. This speed-to-market advantage is especially critical in industries with short product life cycles or intense competition, allowing companies to stay ahead and seize market opportunities.
Customization and Personalization:
Rapid prototyping enables manufacturers to create customized or personalized products. With the ability to rapidly produce individualized prototypes, manufacturers can respond to specific customer requirements and preferences. This capability is particularly valuable in industries like medical devices, automotive, and consumer electronics, where tailored products are in demand.
The Need for Speed in Prototyping
The demand for quick product development has never been greater in today’s competitive market. With time a rare commodity, speed is essential.
Rapidly evolving technologies and increasingly competitive landscapes have meant that businesses must accelerate design-to-market cycles to meet consumer demands and remain at the forefront of their respective industries.
Rapid product development ensures that companies stay agile and responsive but also allows for timely adaptation to changing market trends and emerging opportunities. Beyond just delivering a competitive advantage, quick product development has become the key to sustaining growth, driving innovation, and providing the highest quality standards in precision metal manufacturing.
The Need for Speed in Prototyping
A range of advanced processes have revolutionized rapid prototyping in precision metal manufacturing, each offering unique advantages for faster and more efficient development.
At E-Fab, we specialize in several prototyping processes that include:
Photochemical Etching:
Photochemical etching, also known as chemical blanking or photochemical machining, enables the precise removal of metal material from a sheet through chemical processes.PCE is a highly efficient and cost-effective process. Any tooling change required by a design change is done quickly compared to a process that requires hard tooling that takes more time and costs more labor hours. Also, photochemical etching is ideal for producing intricate, high-precision metal parts. This process is particularly suitable for thin and lightweight components.

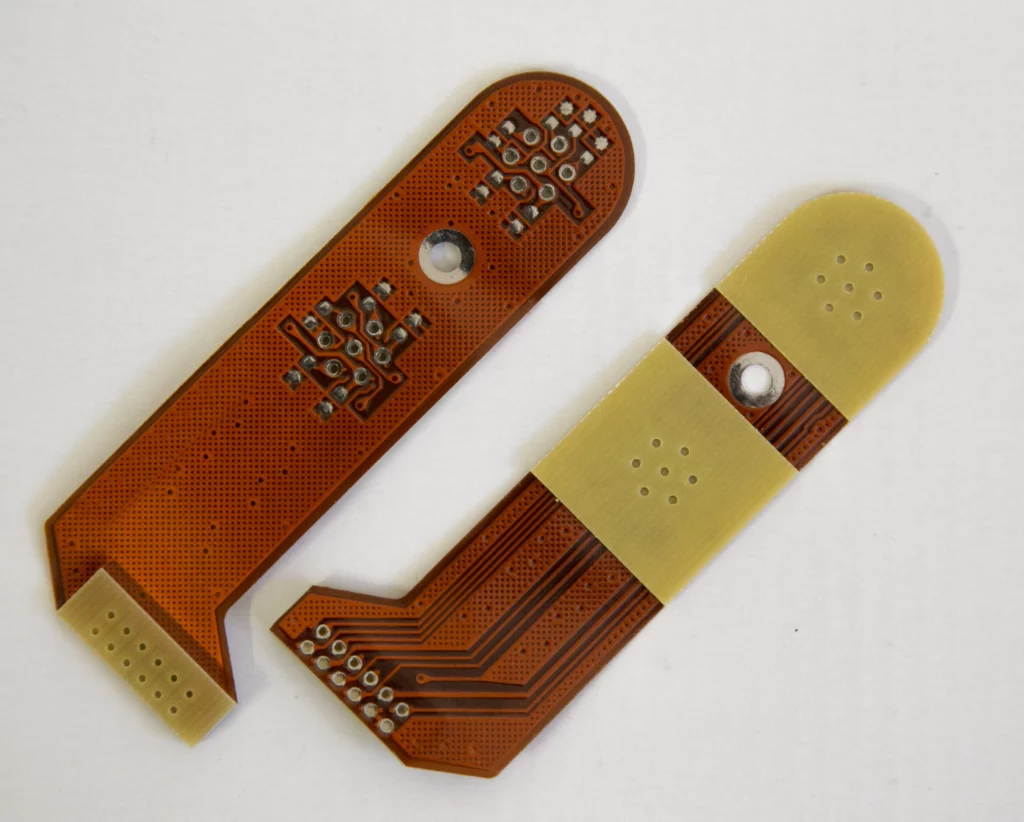
High-Frequency Laminates Processing:
High-frequency laminates, such as printed circuit boards, can be efficiently prototyped using specialized manufacturing techniques. These processes involve the creation of intricate electrical pathways crucial for industries like electronics and telecommunications. High-frequency laminates’ precision and rapid manufacturing capabilities ensure quick validation of electronic components, reducing time-to-market for innovative technologies.

Each of these processes contributes to faster and more efficient metal prototyping by minimizing the need for traditional tooling, reducing material waste, and offering the ability to create intricate and highly accurate metal components.
Material Choices for Rapid Prototyping
The choice of materials for metal prototyping plays a pivotal role in shaping the prototyping process and the final product’s performance.
Different materials offer varying properties, making them suitable for specific applications.
Here at E-Fab, we work with a range of materials in metal prototyping, each with its unique impact on the process:
Copper:
Copper boasts excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties. It’s often the material of choice for prototyping electrical components, such as connectors, busbars, and electronic heat sinks. Its malleability allows for intricate shaping and precise forming, making it ideal for designs requiring complex geometries.
Stainless Steel:
Stainless steel is durable, corrosion-resistant, and strong. It is frequently used in prototyping parts that need to withstand harsh environments, like marine equipment, automotive components, or medical devices. Its robustness ensures the prototypes maintain their integrity throughout testing.
Beryllium Copper:
Beryllium copper combines high strength with electrical conductivity. It’s favored for prototyping springs, contacts, and connectors, where a balance between electrical performance and mechanical stability is essential. Its unique properties contribute to reliable, long-lasting components.
The choice of material can significantly impact the prototyping process. For example, copper simplifies testing for conductivity and thermal performance in electrical components, ensuring that the final product will meet electrical standards. In contrast, using stainless steel in prototyping ensures that parts will endure challenging environments, such as exposure to corrosive elements, which is vital in marine applications or chemical processing. Beryllium copper provides a unique blend of electrical and mechanical properties, making it the go-to choice for parts requiring conductivity and strength.
The Role of R&D in Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping in precision metal manufacturing relies heavily on research and development (R&D). The driving force behind continuous innovation in precision metal manufacturing, R&D enables faster and more efficient prototyping.
Many aspects of prototyping are influenced by research and development, including:
Materials Innovation:
R&D efforts lead to discovering and developing new materials tailored explicitly for precision metal prototyping. For example, researchers might explore advanced alloys or composite materials that offer enhanced strength, durability, or other desirable properties. These innovative materials can then be used to create more efficient and high-performance prototypes.
Advanced Technologies:
R&D teams constantly seek emerging technologies to expedite the prototyping process. For instance, the development of state-of-the-art laser cutting techniques has significantly reduced lead times and enhanced the precision of metal prototypes.

Process Optimization:
Research into process optimization, such as refining photochemical etching or CNC machining techniques, leads to more efficient and cost-effective ways of creating metal prototypes. This results in shorter production cycles and reduced manufacturing costs.
Quality Control:
R&D is crucial in developing advanced quality control methods. For example, the implementation of automated inspection systems utilizing machine learning algorithms can detect defects or deviations in real time, ensuring that prototypes meet the highest standards of precision and quality.
Customization and Adaptation:
R&D allows for the customization of prototyping processes to meet the unique needs of different industries. For instance, in the aerospace sector, R&D teams may focus on developing prototypes that meet strict industry standards and regulations, while in the medical field, the emphasis might be on biocompatible materials and sterile manufacturing processes.
Environmental Considerations:
As sustainability becomes increasingly essential, R&D efforts also focus on developing eco-friendly materials and processes for precision metal prototyping, reducing the environmental footprint of manufacturing.
Communication and Collaboration in Prototyping
Effective communication among designers, engineers, and other stakeholders is the cornerstone of successful rapid prototyping. Clear and collaborative communication ensures all parties understand the project’s objectives, design requirements, and functional expectations. It paves the way for the seamless exchange of ideas, feedback, and insights, facilitating the quick iteration of designs and the timely resolution of any issues that may arise during the prototyping process.
At E-Fab, communication and collaboration are essential, so we focus on facilitating it through physical prototypes and cross-functional teams.
Physical prototypes provide tangible objects to be shared and communicated among stakeholders, including designers, engineers, marketers, and clients. These prototypes facilitate a better understanding of the product’s form, functionality, and aesthetics, fostering effective communication and collaboration. Stakeholders can provide feedback, make suggestions, and identify potential improvements more quickly when they can physically interact with the prototype.
Through our cross-functional teams and a company-wide commitment to problem-solving and innovation, we encourage a prototyping mindset for all our employees. We promote a culture that embraces experimentation, iteration, and learning from failures. By cultivating an environment where rapid prototyping is seen as an integral part of the development process, our employees are more likely to embrace and develop these skills.
The E-Fab Approach to R&D in Rapid Prototyping
Market leaders in rapid prototyping, our company-wide prototyping mindset has seen us lead the way in problem-solving and innovation. And it all starts with our culture. We embrace experimentation, iteration, and learning from failures, cultivating an environment where rapid prototyping is seen as an integral part of the development process.
With a focus on continual improvement, we’re constantly investing in training programs and resources to educate our employees on the latest rapid prototyping techniques and technologies, empowering them to embrace and develop their skills. By providing access to relevant tools and equipment, including computer-aided design (CAD) software, laser cutters, or other prototyping technologies, we’re continually developing our skills to encourage collaboration and build cross-functional teams.
Research & Development is at the heart of our rapid prototyping. We partner with customers to test concepts, materials, and processes with fast prototyping. That process allows parts to undergo testing, analysis, and proofing before mass production. Our in-house engineering team specializes in understanding the goal of each project at the concept stage and then recommends the best choice for materials and manufacturing processes.

The Future of R&D in Rapid Prototyping
As technology advances at an unprecedented pace, R&D efforts will be at the forefront of harnessing emerging tools, materials, and methodologies. With a focus on automation and artificial intelligence, R&D will streamline and optimize the prototyping process, making it faster and more precise than ever.
In this dynamic landscape, R&D will continue to drive innovation, ensuring that rapid prototyping remains at the cutting edge of precision metal manufacturing, delivering high-quality components with unprecedented speed and efficiency.
When it comes to metal prototyping, no one does it better or faster than the trusted team at E-Fab.
Working across a range of leading industries, we partner with customers to test concepts, materials, and processes with fast prototyping. That process allows parts to undergo testing, analysis, and proofing before mass production.
If you’ve got a prototyping problem, let’s solve it!

