To help design engineers enhance their design and manufacturing process, we’ve put together some practical and comprehensive design tips for metal etching.
Metal etching has fast positioned itself at the forefront of today’s manufacturing industry with its ability to produce components with unparalleled versatility, precision, and complexity that traditional machining methods struggled to achieve.

As technology advances, so do the number of processes available for etching metal. From acid etching, laser etching, and laser cutting to chemical etching, photo etching, and other manufacturing processes, there’s a near-endless amount of choice. But, with so many metal fabrication processes available, it can be difficult for design engineers to choose the metal etching process best suited to their project.
To help design engineers enhance their design and manufacturing process, we’ve put together some practical and comprehensive design tips for metal etching to ensure you can get efficient, cost-effective manufacturing for all your metal parts.
The Secrets to Material Selection
When it comes to metal etching, material selection means everything.
Different metals have different metal properties, so the metal surface you choose can significantly affect the metal etching process and the outcome. That’s why it’s essential to understand how the metal etching process works for various metals.
Take aluminum as an example. Widely used in various industries due to its exceptional corrosion resistance and strength, aluminum can be challenging to etch compared to other metals because of its high resistance to chemical attack. While we achieve the same precision with aluminum products, specialized etchants, and processes are often required.
On the other hand, stainless steel is relatively easy to etch due to its softness and low chemical resistance. This makes it attractive for those seeking a cost-effective and efficient metal etching solution.
Copper and its alloys offer excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, making them essential in electronics and electrical applications. The etching of copper is relatively straightforward and finds use in creating intricate circuitry and components.
Titanium is known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and biocompatibility, making it ideal for aerospace and medical applications. However, titanium’s resistance to chemical attack necessitates more aggressive etchants and specialized techniques.
Brass, a copper-zinc alloy, has favorable etching properties, but its composition can vary widely, requiring tailored etching solutions to achieve consistent precision.
Understanding these unique properties is essential to optimize the metal etching process for different applications and produce a smooth, flawless metal surface.

The Importance of Managing Metal Thickness
Managing metal thickness during the etching process can save you time and money. When etching metals, the thicker the metal, the longer it takes to etch.
Choosing the thinnest possible metal thickness for your piece or part is best to save you valuable time and money. Maintaining tolerances with thinner materials is also easier, producing more metal pieces per sheet.
If a component needs thicker metal, it may be necessary to use smaller sheets to achieve tighter tolerances. However, this method would increase the cost due to the additional labor required for handling more sheets.
Chemical milling can reduce the thickness of metals if you can’t access the required thickness from your supplier.
Defining Dimensional Tolerances
Understanding and specifying the required dimensional tolerances at the project’s outset promotes efficiency, quality, and overall success in metal etching processes.
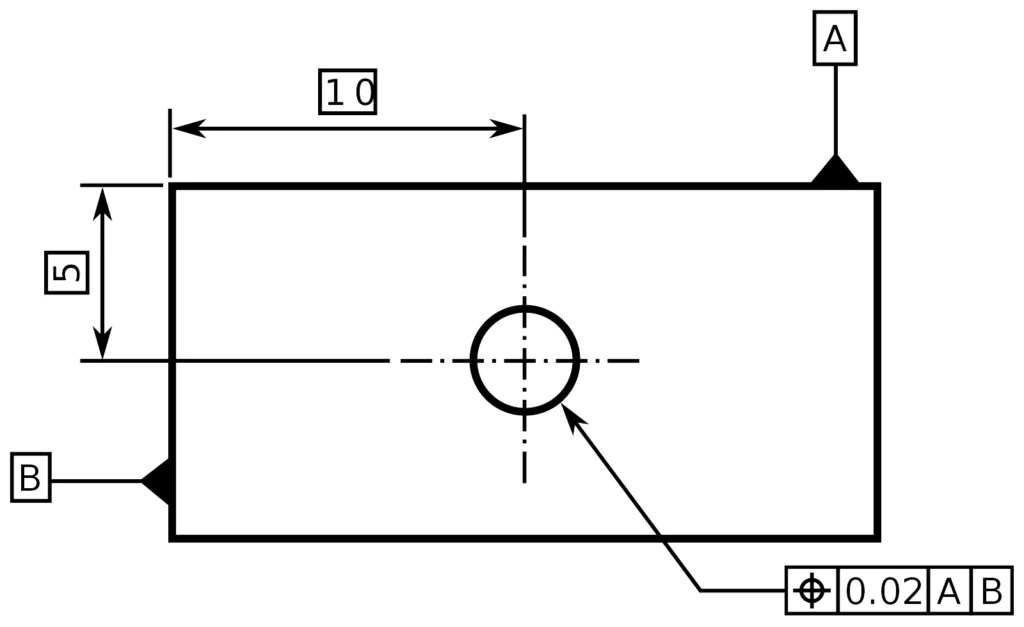
Why? Because dimensional tolerances define the acceptable variations in size, shape, and positioning of metal components during the etching process.
By clearly defining these tolerances early on, manufacturers can ensure that the finished products meet the desired specifications. Failing to establish precise dimensional tolerances can result in costly rework with digital tooling, production delays, and compromised product functionality.
When determining the appropriate tolerances, it’s crucial to consider factors such as material properties, etching technique, and post-etching processes.
Generally, on average for metals > .005" the tolerances are +/- 15% of the metal thickness.
It’s important to have open and effective communication between the design engineers, metal etching specialists, and stakeholders throughout the manufacturing process to achieve accurate and consistent results when etching metal.
Designing for Manufacturability (DFM)
Designed to optimize metal etching and the overall manufacturing process, DFM ensures smoother manufacturing workflows, improved product quality, reduced costs, and faster time-to-market. But what exactly is it?
Design for Manufacturability (DFM) involves considering the manufacturability of a product design early in the development phase. By incorporating these design considerations, engineers can design components and products that are more efficient, cost-effective, and easier to manufacture.
In metal etching, DFM takes into account factors such as material selection, part geometry, tolerances, and metal surface finishes.
By collaborating closely with metal etching specialists, designers can optimize the design to leverage the capabilities and limitations of the etching process. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of dimensional inaccuracies, material waste, and production delays.
Photo etching can enhance Design for Manufacturing (DFM) by offering production speed, design flexibility, and part repeatability. With its precise and efficient process, photo etching allows designers to incorporate intricate geometries and fine details into their designs without the constraints of traditional machining methods. This flexibility allows for innovative and optimized complex designs that can enhance product performance. Moreover, the photo etching process is highly repeatable, ensuring consistent part quality and dimensions from batch to batch. These characteristics make photo etching a valuable tool in DFM, enabling the quick and cost-effective production of complex metal parts while maintaining design integrity and repeatability.
Unique Features of Photochemical Etching
If you’re looking to create unique part features, such as sharp cutting edges and conical openings, for no additional cost, photochemical etching is the process for you.
Unlike traditional machining methods, photochemical etching does not rely on mechanical force or tooling, allowing for the creation of complex shapes and features without incurring additional expenses associated with specialized tooling or secondary operations.
Due to the inherent edge “cusp” of chemical etching, engineers can design products with unique characteristics. This includes the ability to etch sharp cutting edges, which are crucial for applications like surgical instruments or precision blades. Additionally, photochemical etching can produce conical openings with precise angles and dimensions, enabling the creation of parts with enhanced functionality and performance.
The cost-effectiveness of photochemical etching in creating these unique part features makes it an attractive choice for industries seeking high-quality, customized components without incurring additional manufacturing costs.
Prototyping and Design Modifications

In sheet metalworking, it is generally true that the more complex the part, the higher the cost due to the need for expensive and intricate tooling. When traditional etching methods are used on non-standard materials, thicknesses, and grades, costs can also become more expensive. However, chemical milling costs remain unaffected by these factors.
If you’re an engineer seeking intricate and precise metal parts and components, chemical etching has quickly become the choice process. It can handle challenging geometries and provides great flexibility, allowing you to make design adjustments even during manufacturing.
The photochemical etching process also delivers economical prototyping. Utilizing a photoresist pattern to remove metal selectively allows for the simultaneous etching of multiple parts with varying designs and dimensions. Unlike traditional machining methods that require separate setups and tools for each component, photochemical etching can accommodate a range of geometries within a single etching run. This capability eliminates the need for multiple tools, reduces production time, and minimizes associated costs.
Common Pitfalls in Metal Etching Design
To ensure precise and efficient metal etching across various metals, it’s important to understand and avoid some of the common design mistakes that can impact the etching process.
One of the most common mistakes is not considering the material thickness. An important part of the process, as we mentioned earlier, it’s crucial that designers ensure that the chosen metal thickness is suitable for the etching process, as excessively thin or thick materials can result in etching difficulties or dimensional inaccuracies.
Another common pitfall lies in failing to provide adequate spacing between features. Insufficient spacing can lead to overlapping or merging etched areas, compromising the desired design.
Additionally, inadequate consideration of fillets and radii can result in stress concentrations during etching, causing premature failure of the part.
To avoid these common mistakes, designers should collaborate closely with metal etching specialists throughout the process and gain a thorough understanding of etching capabilities and limitations.
Become a master of manufacturability
As technology advances, innovative etching methods and chemistries continue to be developed, enabling even more intricate and precise metal components to be produced. But, with so many choices, deciding what metal etching process is best for your metal surface can be hard. Luckily, as we’ve outlined, you need to consider a few key things to ensure you receive efficient, precise, and cost-effective manufacturing for all your metal parts.
Apply the shared design tips to your manufacturing processes and dive deeper into the ever-evolving world of metal etching to see what’s truly possible for your business.

